論説

概要
- While US banks still rely heavily on credit and debit cards for revenue and customer relationships, alternative payment methods are expanding rapidly in many other countries.
- Even in the US, consumer preferences—particularly among younger generations—have been shifting to digital wallets, buy-now-pay-later services, and peer-to-peer payment methods.
- These trends raise the stakes for banks around future card revenues, cross-selling opportunities, and customer loyalty.
- To remain competitive, US banks must enhance the overall customer experience, modernize technology, integrate alternative payment options, break through the silos of payments organizations, and use data and generative artificial intelligence to personalize offerings.
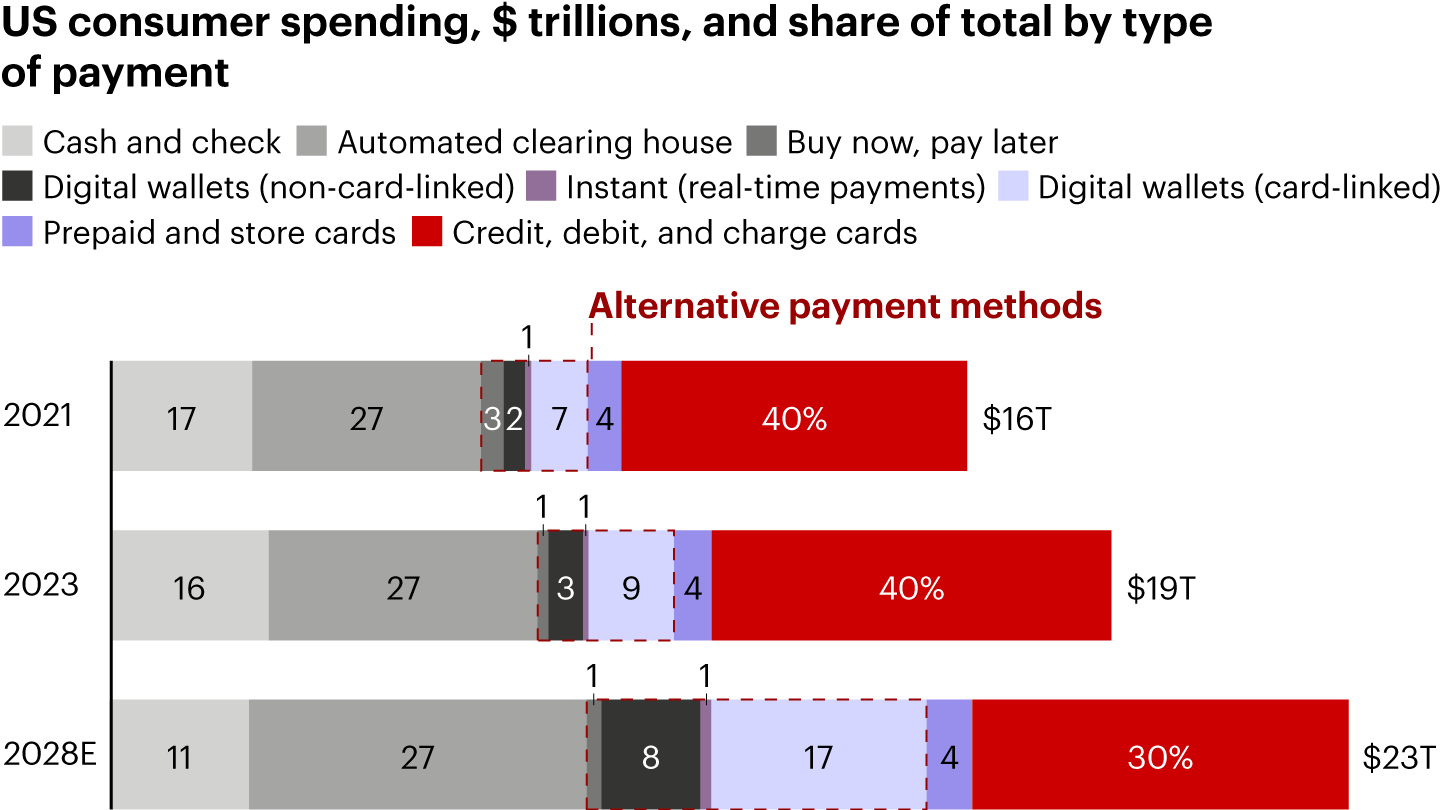
US banks rely on credit and debit cards as an anchor for customer relationships, and as a gateway to other sources of profitable revenue. By 2028, US card revenues are expected to reach roughly $400 billion, 10% higher than in 2023. Fueling that growth is a combination of consumers’ enthusiasm for rewards programs, a surge in e-commerce transactions, and the rising use of cards for business-to-business payments.
Card growth also stems from US consumers being slower to adopt alternative payment methods compared to other countries such as the Nordics, Singapore, Brazil, and China. In these regions, the rapid adoption of alternative methods has resulted from government support for a real-time payments network, lower transaction costs, and better user experiences.
For US banks, the stakes are high. Digital wallets, buy-now-pay-later services, and account-to-account systems, such as Zelle and Venmo, have gained market share. In addition, the recent US election adds uncertainty around the future of card regulation; for instance, will the government favor retailers or card issuers?
Alternative payment formats will continue to expand faster in the US than card payments themselves (see Figure 1). Finding new sources of growth will become increasingly important for US banks, so it pays for them to monitor how alternative payment methods are playing out globally.

Make it easy, convenient, and digital
Consumers increasingly value easy, convenient digital experiences, which partly explains why they’re more satisfied with the offerings from insurgent companies, as measured by Net Promoter Score℠, a key metric of loyalty, through an NPS Prism® survey (see Figure 2). Banks and other traditional providers risk losing ground to technology firms that increasingly dominate the customer interface via their app or their digital wallets. For instance, Apple Pay’s user base of roughly 61 million subscribers in 2024 is projected to grow to over 82 million by 2030.
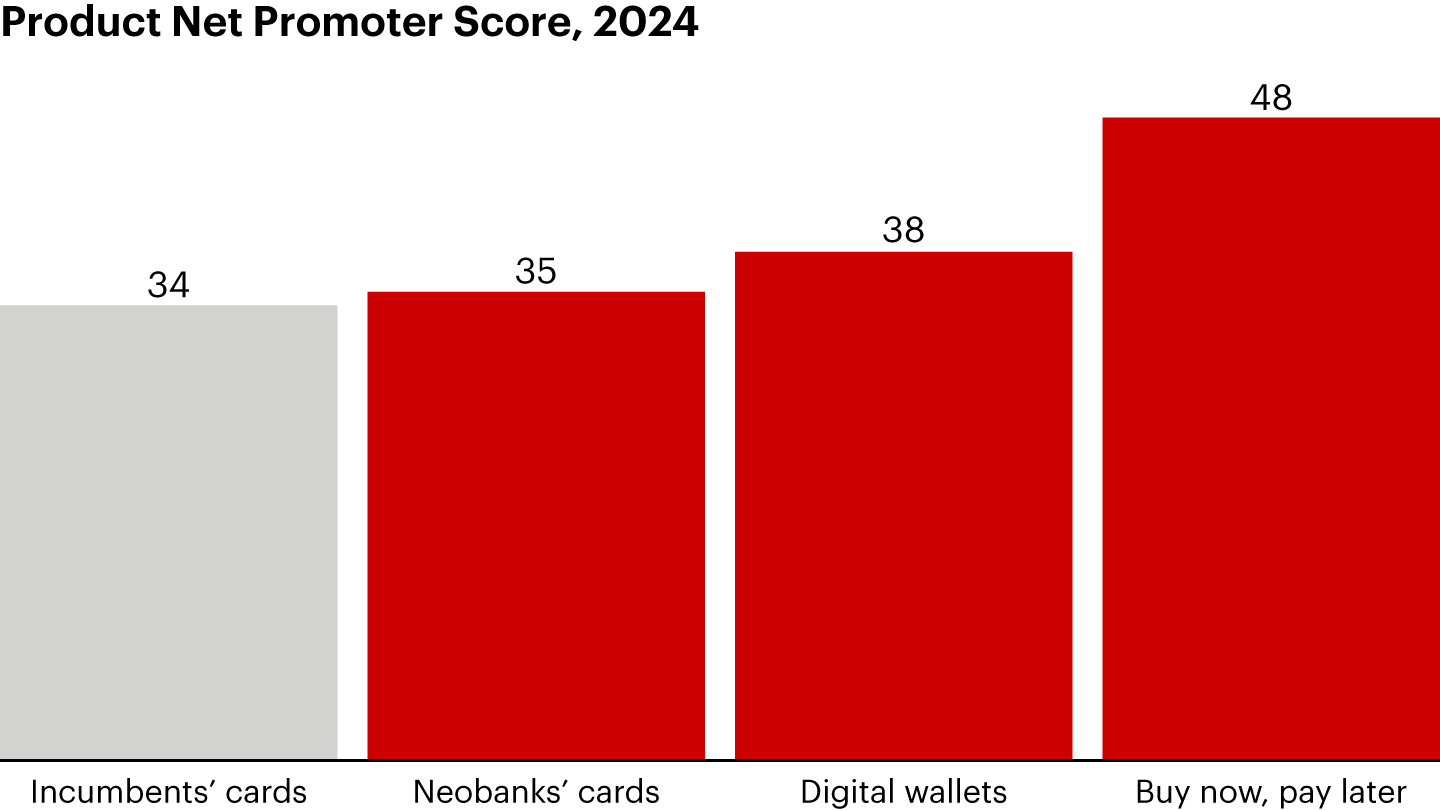

There’s a demographic risk for incumbent banks in these trends, since around 40% of their card customers belong to the millennial or Generation Z cohorts, as shown by a recent NPS Prism survey. Younger consumers have been the most avid users of buy-now-pay-later offerings and digital wallets, raising the stakes for banks around future card revenues, cross-selling opportunities, and customer loyalty (see Figure 3).


To be sure, new payment methods also appeal to many in the Generation X and baby boomer cohorts, as seen by the slightly higher or roughly equivalent Net Promoter Scores they give to neobanks, digital wallets, and buy-now-pay-later services compared to younger generations. The risk for card issuers is even broader, as having primacy on cards helps a bank strengthen customer loyalty across other products as well. Companies with credit card primacy have a nine-percentage-point-higher Net Promoter Score than companies without primacy, according to the NPS Prism survey.
Building resilience in payments
The good news for banks is that they lead insurgent competitors in preventing fraud and resolving disputes—capabilities built on trusted infrastructure that will be crucial for maintaining good customer relationships. Still, banks must strengthen traditional card-based offerings while embracing alternatives. They can stay relevant by taking the following steps.
- Elevate the customer experience. This involves focusing first on such moments of truth as adjusting limits, handling a missed payment, or processing an application for a card (see Figure 4). It also requires tailoring propositions for individual customer segments; some segments, for instance, prefer cash-back offers, while others prefer miles-based cards. A better experience hinges on banks having a deep understanding of priorities for each target segment in order to personalize different features, including elements of their loyalty program.
Figure 4Card issuers should focus on moments of truth that can create promoters or detractors 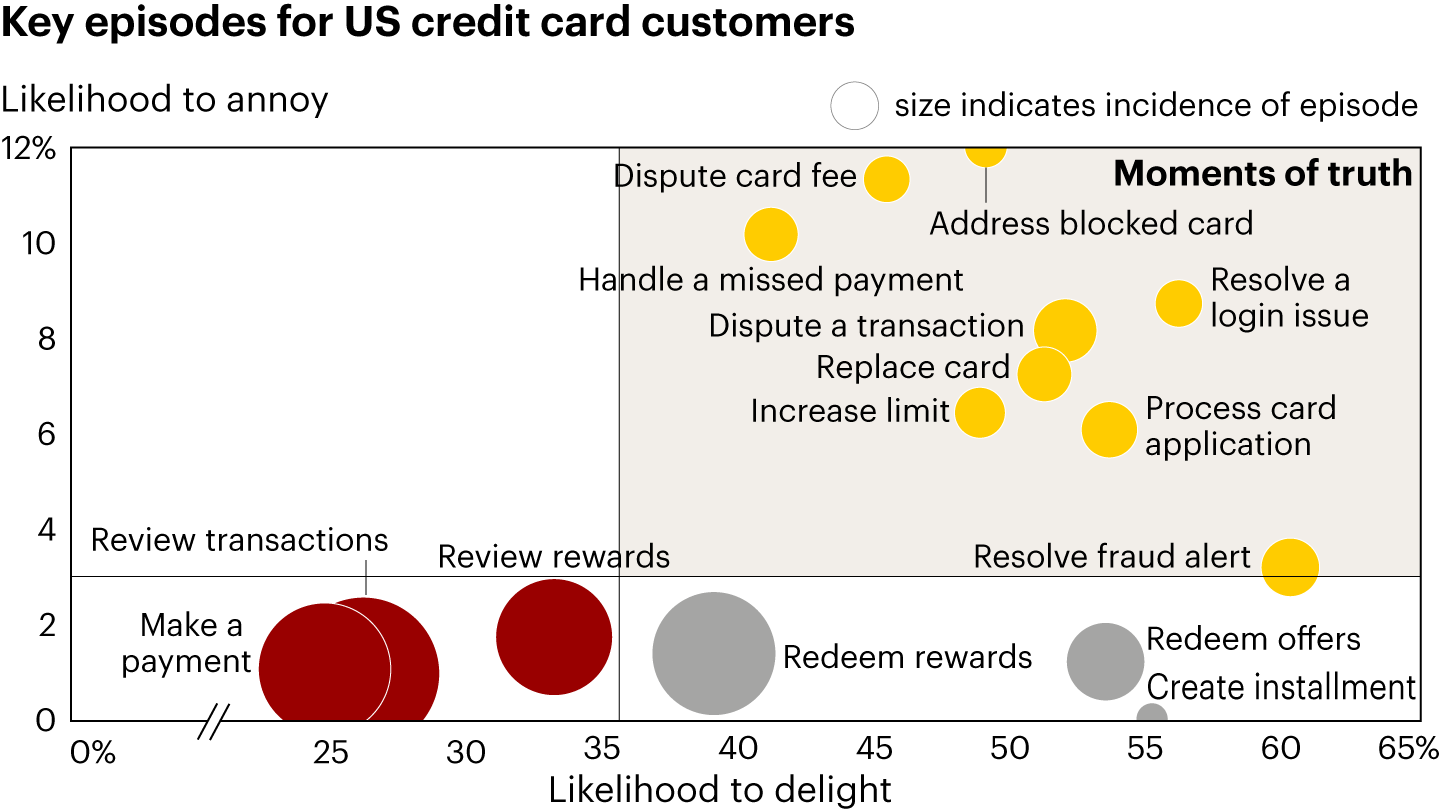

出所 NPS Prism US Consumer Banking and Payments Survey, 2024 (n=4,382) - Integrate alternative payment methods. Giving customers more flexibility will boost their engagement. Nubank in Brazil allows customers to initiate an account-to-account transaction using Pix, Brazil’s real-time payment rail, but fund it with a card-based installment plan; more than 35% of their active credit card customers used the Pix financing feature in 2023.
For US banks, Apple’s opening the iPhone’s NFC chip to third-party developers allows for contactless transactions outside of Apple Pay and Apple Wallet. Banks can now develop their own NFC-based payment solutions for the iPhone, giving them a route to win back the customer interface. - Use data to personalize offerings and improve risk assessments. Open banking allows card issuers to use new internal and external data pools. Banks can go beyond traditional credit scoring methods to use open finance and alternative data such as rental payment records and smartphone app usage, thereby building highly predictive risk assessments. And card issuers can create their own commerce media networks within their apps to promote products directly to consumers and tap into other revenue sources.
- Incorporate generative artificial intelligence (AI). Generative AI technologies are already transforming payments, from setting up accounts, to analyzing customer spending, to providing shopping recommendations. Mastercard integrated generative AI into fraud detection in 2024. So far, the company has doubled its detection rate for compromised cards before they can be used fraudulently and has tripled the speed of identifying merchants at risk.
- Rationalize the organization. Banks typically have a dedicated group for card products. To make the most of alternative payment systems, they should consider a customer-centered approach that organizes around all types of payment-related needs, regardless of the product or payment rail.
- Modernize the processing infrastructure. A more flexible technology stack will reduce process complexity and manual work, and more easily integrate services, such as combining a checking account with a credit card account. This type of contemporary system is able to quickly accommodate new features that improve the customer experience, and interface easily with external partners when necessary.
Demand for payments in the US will continue to shift toward digital wallets, peer-to-peer services, and account-to-account transactions. For banks, staying competitive will require more than incremental adjustments. They will have to update loyalty programs, modernize technology, and leverage data to provide personalized propositions to their target customer segments. Those banks that adapt their payments strategies will benefit from robust growth in this market, along with enhanced customer loyalty and the cross-selling opportunities that come with it.
NPS Prism®
Our cloud-based customer experience benchmarking service that provides actionable insights and analysis that guide your creation of game-changing customer experiences.